Real Celebrities Never Die!
OR
Search For Past Celebrities Whose Birthday You Share

source:https://en.wikipedia.org
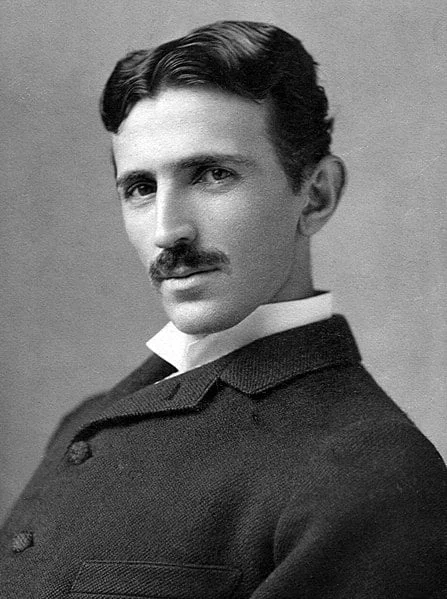
Nikola Tesla
Birthday:
10 Jul, 1856
Date of Death:
07 Jan, 1943
Cause of death:
Heart failure
Nationality:
Serbian-American
Famous As:
Electrical engineer
Age at the time of death:
86
Nikola Tesla's Quote's
Introduction: A Visionary Inventor
Nikola Tesla was a Serbian-American inventor, electrical engineer, and futurist who made significant contributions to the development of modern electrical systems.
Early Life and Fascination with Electricity
Nikola Tesla was born on July 10, 1856, in the village of Smiljan, which was then part of the Austrian Empire (modern-day Croatia). His early years were marked by a deep fascination with electricity, and he often witnessed electrical phenomena in his environment.
Early Career and the Induction Motor
In 1881, Tesla moved to Budapest, Hungary, where he worked for a telegraph company. While there, he conceived the idea of the induction motor, which revolutionized the field of electrical power. In 1884, Tesla relocated to the United States, settling in New York City.
Conflict with Edison and Founding Tesla Electric Company
During his time in the U.S., Tesla worked for Thomas Edison’s Edison Machine Works. However, their differing approaches to electrical power led to disagreements, and Tesla eventually left Edison’s company. In 1887, he established his own laboratory and formed the Tesla Electric Company, where he began to explore his ideas for alternating current (AC) electrical systems.
Development of the AC Electrical System
Tesla’s work on AC systems gained widespread recognition, and in 1888, he was granted multiple patents for his inventions related to AC induction motors, transformers, and other devices. These patents formed the foundation for the development of the polyphase AC system, which allowed for the transmission of electricity over long distances more efficiently.
Hydroelectric Power Plant at Niagara Falls
In 1891, Tesla constructed the first hydroelectric power plant at Niagara Falls, demonstrating the feasibility of transmitting AC power over long distances. This achievement solidified AC as the dominant system for electrical power generation and distribution, displacing Edison’s direct current (DC) system.
Inventions and Wireless Experiments
Throughout the 1890s, Tesla continued to make significant contributions to electrical engineering. He invented the Tesla coil, a device used to generate high-voltage, high-frequency alternating currents. He also conducted experiments in wireless power transmission and wireless communication, envisioning a world where electricity could be transmitted wirelessly through the air.
World’s Columbian Exposition
In 1893, Tesla presented his ideas and inventions at the World’s Columbian Exposition in Chicago, where he demonstrated wireless lighting and the principles of wireless power transmission. His achievements at the exposition further established his reputation as a brilliant and visionary inventor.
The Wardenclyffe Tower Project
In the early 1900s, Nikola Tesla began working on his most ambitious project, the Wardenclyffe Tower. Intended as a wireless power transmission station, the tower was designed to transmit electricity wirelessly to any point on Earth. However, due to financial difficulties, the project was never fully realized, and the tower was eventually demolished.
Later Inventions and Research
Despite setbacks, Tesla continued his research and inventions in various fields. He developed the concept of the “Tesla turbine”, an efficient and compact rotary engine design. He also explored the possibility of harnessing cosmic rays for practical applications and conducted experiments in radio-controlled boats and submarines.
Challenges in Later Years
In his later years, Tesla faced financial challenges and struggled to secure funding for his projects. He lived a relatively reclusive life, but his contributions to science and technology continued to inspire future generations of inventors.
Legacy of Nikola Tesla
Nikola Tesla passed away on January 7, 1943, in New York City at the age of 86. His ideas and inventions had a profound impact on the world, laying the groundwork for modern electrical power systems and wireless communication technologies. Today, Nikola Tesla is remembered as one of the greatest inventors in history, known for his brilliant mind and his relentless pursuit of scientific innovation.
Name:
Nikola Tesla
Popular Name:
Nikola Tesla
Gender:
Male
Cause of Death:
Heart failure
Spouse:
Place of Birth:
Smiljan, Croatia
Place of Death:
New York City, U.S.
Occupation / Profession:
Personality Type
Advocate Quiet and mystical, yet very inspiring and tireless idealists. He devoted his whole life for his ideals.
He developed the idea for smartphone technology in 1901
Nikola Tesla was born during a fierce lightning storm in July 1856. According to family legend, the midwife declared this a bad omen, but Tesla's mother replied: "No. He will be a child of light."
Tesla and American author Mark Twain were close friends. In 1894, Tesla took one of the first photographs ever lit by phosphorescent light, featuring Twain as the subject
Tesla claimed the idea of alternating currents came to him in a vision. He later developed this concept into the basis of most AC machinery, revolutionizing electrical power systems.
Tesla invented the world's first remote-controlled device - a small boat operated via radio waves - which he demonstrated at Madison Square Garden in 1898
Edison Medal (1916)
Elliott Cresson Medal (1894)
John Scott Medal (1934)
Order of Prince Danilo I (1895)
Order of St. Sava, II Class, Government of Serbia (1892)
Order of the White Eagle, I Class, Government of Yugoslavia (1936)
Order of the Yugoslav Crown (1931)